Every great website tells a story — not just through its words or visuals, but through the way it’s structured, optimized, and presented to search engines. That process begins with On-Site SEO, the invisible architecture that helps search engines understand your content and users enjoy every second they spend on your site. Before diving deeper, it’s essential to understand how On-Site SEO fits within the broader framework of search optimization. If you’re new to this, you can first explore the foundational guide on search engine optimization — it will help you see how all SEO components work together to boost visibility and authority.

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover everything you need to know about On-Site SEO — from what it is and why it matters, to advanced techniques that top marketers use to climb Google rankings. We’ll connect theory with action, weaving real-world examples and practical checklists so entrepreneurs, marketers, and content strategists can turn SEO from a concept into a competitive advantage.
What Is On-Site SEO?
On-Site SEO (also known as on-page SEO) refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages so they rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. It’s about making your content discoverable, understandable, and valuable — both for search algorithms and for human readers. This section should define On-Site SEO clearly, highlight how it differs from other types of optimization, and explain how elements like meta titles, headings, content quality, image optimization, and internal linking form the backbone of a well-optimized page.
Importance of On-Site SEO
Imagine you’ve opened a beautiful shop with premium products — but the shelves are unorganized, labels unclear, and customers can’t find what they need. Even if people walk in, they leave confused. That’s exactly what happens when a website lacks On-Site SEO.
On-Site SEO (or On-Page SEO) is the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their visibility and relevance for search engines and users. It focuses on everything within your website — from the words on your page to the way your code is structured.
The goal is simple: help search engines understand what your page is about and show it to the right audience. Key components include meta titles, descriptions, headings, URLs, internal links, images, and overall content quality. When these elements work in harmony, your site becomes both easier to crawl and more compelling to read.
Search engines like Google are in the business of delivering the best answers. They scan millions of pages to find those that not only match a query but also provide value. Without On-Site SEO, even the most insightful content risks being invisible.
For businesses and marketers, strong On-Site SEO brings three major benefits:
- Visibility: Proper optimization increases the chances of your content appearing in top search results.
- User Experience: A well-structured website makes it easy for visitors to find information, stay longer, and convert.
- Authority: Over time, well-optimized content earns trust from both readers and algorithms — strengthening your brand’s digital presence.
In short, On-Site SEO bridges the gap between what your audience searches for and what your business offers.
Types of On-Site SEO
Not all optimization happens the same way. On-Site SEO can be grouped into three broad categories:
1. Content Optimization
This includes improving written content to align with search intent, using relevant keywords naturally, and ensuring each page provides unique value. Engaging writing, strong headings, and internal linking make content easier to digest — and rank.
2. HTML Optimization
HTML tags communicate structure and meaning to search engines. This includes:
- Title Tags: Defining page topic.
- Meta Descriptions: Encouraging clicks from search results.
- Header Tags (H1-H6): Organizing content hierarchy.
- Image Alt Text: Describing visuals for both SEO and accessibility.
3. Technical Optimization
While this overlaps slightly with Technical SEO, the focus here is on ensuring fast loading speeds, mobile-friendly design, secure HTTPS connections, and proper URL structure.
Think of Technical SEO as the engine that keeps your site running smoothly, while On-Site SEO is the steering wheel that helps guide the journey.
Key On-Site SEO Ranking Factors (In-Depth Guide)
Search engines have evolved from simply reading keywords to understanding intent, context, and user satisfaction. Today, Google’s algorithm evaluates hundreds of signals to determine whether your page deserves a top position — but at its core, it still values clarity, structure, and user-centric optimization. Below are the most influential On-Site SEO ranking factors, explained in practical depth so you can take direct action.
1. High-Quality Content: The Heart of On-Site SEO
Search engines were built to serve users — not websites. That means your content must deliver real value before it can earn visibility. High-quality content is informative, original, and purpose-driven. It addresses a clear problem or need and provides insights that users can’t easily find elsewhere.
Here’s how to achieve that:
- Understand user intent: Every page should match what people expect when they click. If someone searches “best email marketing tools,” they want comparisons — not theory.
- Use storytelling: Instead of dumping data, weave examples, scenarios, or lessons that build trust and engagement.
- Maintain clarity: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and subheadings to keep readers moving smoothly through your content.
- Keep it updated: Regularly refresh outdated statistics or examples — freshness boosts ranking signals.
Pro Tips: Google’s Helpful Content system prioritizes pages that demonstrate expertise, experience, authority, and trust (E-E-A-T) — so showcase real insights of your content, not surface-level summaries.
2. Keyword Placement: Strategic and Intent-Based
Keywords are still the foundation of search visibility — but they work best when placed purposefully, not forcefully. The placement and context of your keywords tell search engines exactly what your page covers.

Where to include primary keywords:
- Title tag (preferably at the beginning)
- Meta description
- URL slug
- First 100–150 words of content
- At least one H2 or H3 subheading
- Naturally throughout the body text
Also, use semantic keywords or LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) terms — related phrases that help Google interpret meaning. For example, for “On-Site SEO,” semantic terms include “on-page optimization,” “meta tags,” “keyword density,” or “internal linking strategy.”
Pro Tips: Avoid over-optimization. Instead of repeating the same keyword ten times, use contextually similar terms that sound natural.
3. Title Tags & Meta Descriptions: Your First Impression
Before users even click, your title and meta description are what convince them to visit your page. A great title should be:

- Concise (under 60 characters)
- Keyword-rich (but natural)
- Emotionally engaging (use power words like “guide,” “strategies,” “best”)
Example:
Good: “On-Site SEO: Complete Guide to Optimize Your Website”
Poor: “On-Site SEO, Website SEO, SEO Optimization for Website”
The meta description (155–160 characters) serves as your elevator pitch. It should summarize what readers will gain — and include a soft call to action, such as “Learn how to boost your website’s visibility with these proven On-Site SEO strategies.”
Pro Tips: Google sometimes rewrites meta descriptions if it thinks yours doesn’t match intent — so make sure your content aligns closely with your metadata.
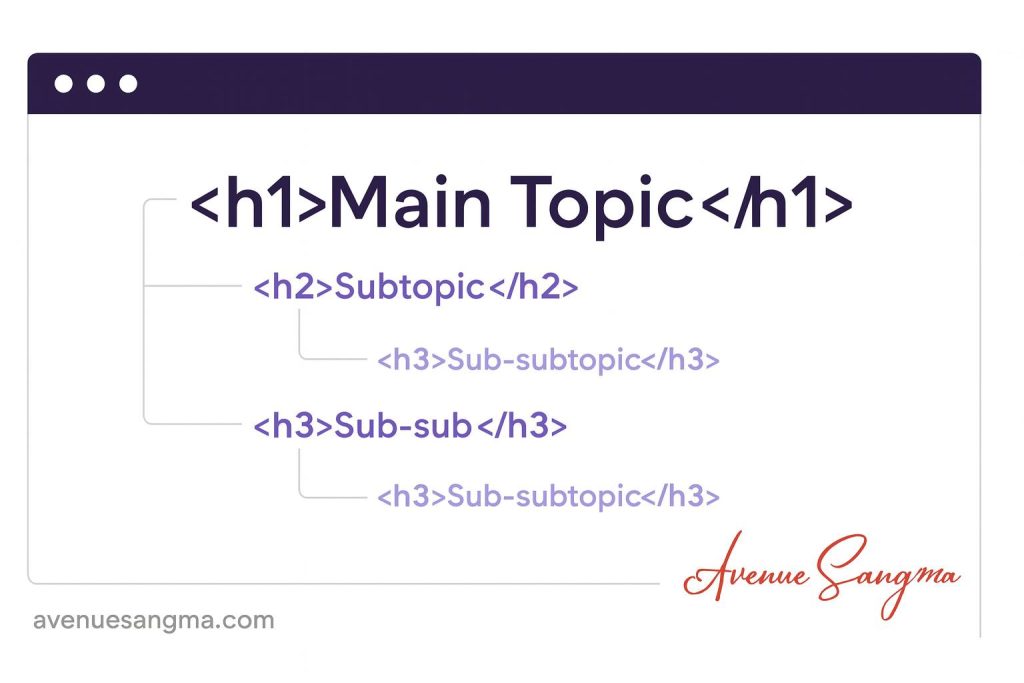
4. Header Tags & Readability: The Structure That Guides Both Users and Bots
Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are not just visual dividers; they’re semantic signals. They help Google interpret your content’s hierarchy and help readers navigate effortlessly.
Best practices:
- Use one H1 per page (usually the main title).
- Break sections with H2s for major topics and H3s for subtopics.
- Include keywords naturally in a few headers but avoid stuffing.
- Keep sentences concise — aim for an average sentence length of 15–20 words.
For readers, good structure equals better comprehension. For algorithms, it means easier scanning and topic association. The result: higher engagement and improved rankings.
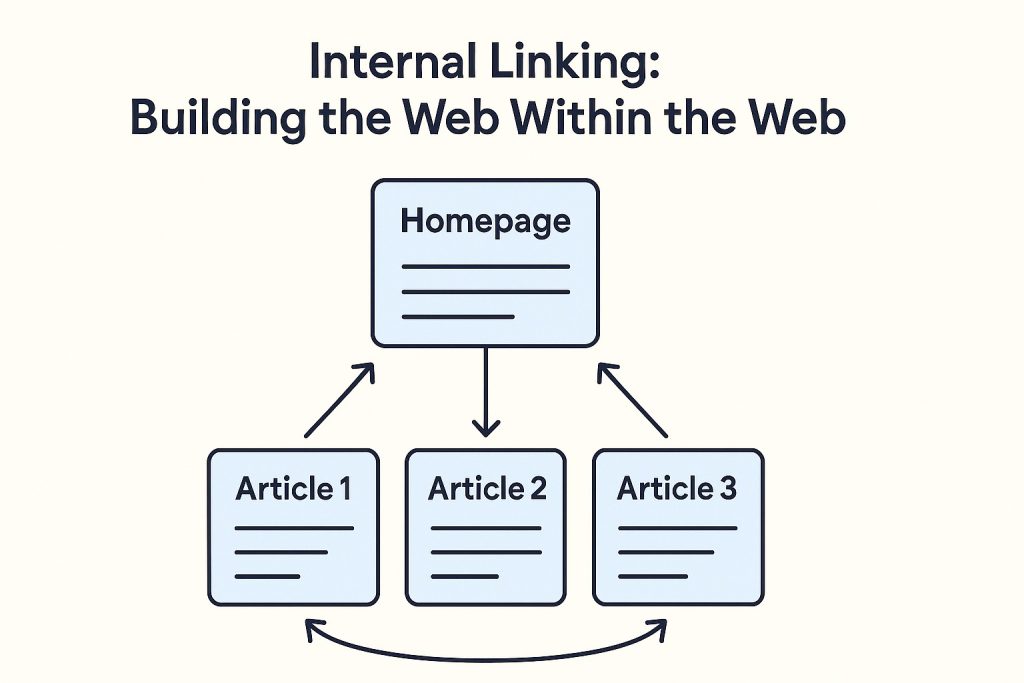
5. Internal Linking: Building the Web Within the Web
Internal linking is like giving your website a circulatory system. It distributes authority (“link juice”) and helps users explore related topics without leaving your site.
Strong internal linking practices:
- Use descriptive anchor text that tells readers (and Google) what to expect.
Example: Instead of “click here,” use “learn how to optimize anchor text effectively.” - Link to pillar pages or high-value resources — not just random articles.
- Keep your link structure shallow: important pages should be accessible within three clicks from the homepage.
- Audit regularly to fix broken or outdated links.
Pro Tips: Internal linking is one of the most underrated ranking factors — it improves both UX and SEO simultaneously, helping Google index your pages more efficiently.
6. Image Optimization: Visuals That Work for SEO
Images play a big role in engagement and ranking performance. But if they’re heavy or poorly tagged, they slow down your site — hurting user experience and SEO.
Optimize images by:
- Compressing file size without losing quality (use tools like TinyPNG or Squoosh).
- Naming files descriptively:
on-site-seo-checklist.jpginstead ofIMG1234.jpg. - Including alt text that describes the image contextually for search engines and visually impaired users.
- Using the WebP format when possible — it loads faster and supports better compression.
Pro Tips: Optimized visuals can appear in Google Image Search — adding another entry point for organic traffic.
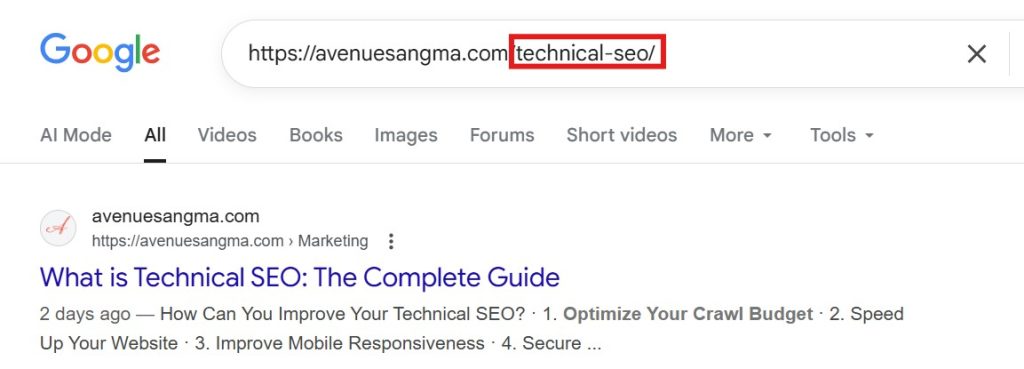
7. URL Structure: Clean, Descriptive, and Consistent
A well-structured URL is simple, keyword-focused, and logical. It tells both users and crawlers exactly what the page is about.
Effective URL structure tips:
- Keep it short and descriptive (under 75 characters).
- Use lowercase letters and hyphens (not underscores).
- Avoid unnecessary parameters, numbers, or session IDs.
- Align URL hierarchy with your content silo structure (e.g.,
/seo/on-site-seo/under/seo/).
Good URLs not only improve click-through rates but also create a stronger site architecture that supports long-term scalability.
8. Page Experience: The Modern Ranking Signal
User experience (UX) is a ranking signal that can make or break your SEO strategy. Google’s Core Web Vitals measure how users feel while interacting with your site.
Page Experience is a key Google ranking signal emphasizing user satisfaction, site speed, and interactivity. Learn how performance impacts SEO with Chrome Developers’ speed insights and test your site using PageSpeed Insights.
The three key metrics are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How quickly your main content loads (should be under 2.5 seconds).
- First Input Delay (FID): How fast your site reacts to user interaction (under 100ms).
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How stable your page elements are while loading (below 0.1).
To improve page experience:
- Use a reliable hosting provider and CDN (Content Delivery Network).
- Optimize images, videos, and scripts to reduce load times.
- Ensure mobile responsiveness and intuitive navigation.
- Eliminate intrusive pop-ups or ads that disrupt reading.
Pro Tips: Even if your content is top-tier, poor user experience can drag rankings down — Google rewards websites that deliver both relevance and satisfaction.
Each of these factors works like an instrument in an orchestra — individually useful, but truly powerful when synchronized. High-quality content gives your site meaning, keyword optimization gives it direction, and technical polish ensures it performs flawlessly.
A well-optimized website doesn’t just rank; it converts. Visitors stay longer, share more, and eventually trust your brand as an authority in its niche.
Conducting Keyword Research for On-Site Optimization
Keyword research is the foundation of every successful On-Site SEO strategy. It tells you what your audience is searching for and helps you craft content that meets their intent.
Step 1: Understand Search Intent
Every keyword has a purpose — informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial. Knowing the intent behind a search term ensures your content aligns with user expectations.
Step 2: Identify Primary & Secondary Keywords
Use SEO tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or Ubersuggest to find relevant keywords. Primary keywords target the main theme, while secondary keywords support it and help capture long-tail traffic.
Step 3: Map Keywords to Pages
Avoid keyword cannibalization by assigning distinct keywords to each page. One main keyword per page keeps the site architecture clear.
Step 4: Optimize Anchor Texts
When linking internally, use descriptive and natural anchor texts. This helps Google understand page relationships. To learn how to do this effectively, check out the detailed guide on anchor text — it shows how choosing the right link words can significantly improve authority and ranking signals.
Keyword research doesn’t end with selection; it evolves with data. Review your analytics periodically to see which terms are driving engagement and adjust accordingly.

Final On-Site SEO Checklist
Before hitting “publish,” run through this comprehensive checklist:
| Category | Checklist Item |
|---|---|
| Content | Target keyword appears in title, intro, and throughout naturally |
| Content provides real value, not fluff | |
| Readability score is above 60 (Flesch scale) | |
| HTML Structure | H1 includes main keyword |
| Subheadings (H2-H3) organize content logically | |
| Meta description is optimized (155-160 chars) | |
| Technical | Page loads under 3 seconds |
| Mobile-friendly and HTTPS secured | |
| Clean URL with no unnecessary parameters | |
| Images & Links | Alt tags added to all images |
| Internal links to relevant pages (2-4 per post) | |
| External links to credible sources | |
| UX & Engagement | Short paragraphs (2-4 lines each) |
| CTA (Call to Action) at logical points | |
| Schema markup added (if applicable) |
Using this checklist consistently ensures your content performs better over time — not just once.
On-Site SEO vs Off-Site SEO: Understanding the Core Differences
When it comes to search engine optimization, every successful strategy stands on two strong pillars — On-Site SEO and Off-Site SEO.
They work like two halves of a complete system: one focuses on optimizing what’s within your website, and the other strengthens your authority beyond it.
To rank higher and build lasting visibility, you must balance both. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their differences, roles, and how they complement each other.
Definition and Focus
| Aspect | On-Site SEO | Off-Site SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of optimizing elements within your website to improve its visibility and relevance for search engines. | The process of enhancing your website’s reputation, trust, and authority through actions that happen outside your website. |
| Focus Area | Internal factors — content quality, structure, user experience, and technical performance. | External signals — backlinks, social engagement, and brand mentions across the web. |
Primary Goal
| On-Site SEO | Off-Site SEO |
|---|---|
| Optimize content, design, and user experience to rank higher for relevant keywords. | Build domain authority, credibility, and external signals to strengthen trustworthiness. |
Insighst:
Think of On-Site SEO as making your website worthy of ranking, while Off-Site SEO is what convinces others (and Google) that it deserves to rank.
Key Ranking Activities
| On-Site SEO Tasks | Off-Site SEO Tasks |
|---|---|
| – Keyword research & placement – Title tags & meta descriptions – Content optimization & readability – Internal linking strategy – Image optimization – Page load speed improvement – Schema markup & structured data – Mobile-friendliness & UX – Clean URLs – XML sitemap setup | – Link building (quality backlinks) – Guest posting & collaborations – Content marketing distribution – Social media engagement – Influencer marketing – Brand mentions & citations – Online PR & outreach – Reviews & local SEO listings – Podcast or media exposure |
Control and Responsibility
| On-Site SEO | Off-Site SEO |
|---|---|
| 100% under your control — you can edit, test, and optimize directly. | Partially under your influence — you can’t force backlinks or social mentions; you must earn them. |
Example:
You can improve your page speed instantly (On-Site), but earning backlinks from high-authority domains (Off-Site) takes consistent outreach and credibility.
Impact on Search Algorithms
| On-Site SEO | Off-Site SEO |
|---|---|
| Signals relevance — helps search engines determine what your website is about. | Signals authority — helps search engines decide how trustworthy your website is. |
Insights:
Relevance without authority means you’ll be understood but not prioritized. Authority without relevance means you’ll be powerful but invisible in the wrong searches.
Both signals must align.
Metrics to Measure Success
| On-Site Metrics | Off-Site Metrics |
|---|---|
| – Organic traffic growth – Average session duration – Bounce rate – Keyword ranking improvements – Click-through rate (CTR) – Page speed & Core Web Vitals | – Number and quality of backlinks – Domain authority (DA) or domain rating (DR) – Referral traffic – Brand mentions – Social shares and engagement – Local citations or reviews |
Use tools like Google Search Console for On-Site performance and Ahrefs or SEMrush for Off-Site metrics.
Common Misconceptions
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| “Off-Site SEO alone can make my site rank.” | Without On-Site optimization, backlinks won’t help — Google must first understand your site. |
| “On-Site SEO is enough if my content is great.” | High-quality content still needs authority signals (links, shares, mentions) to outperform competitors. |
| “SEO is a one-time fix.” | SEO is continuous. Algorithms evolve, and both on-site and off-site strategies must adapt. |
Advanced Strategies for Both
| Advanced On-Site SEO | Advanced Off-Site SEO |
|---|---|
| – Entity optimization using schema – Topic clustering and internal link sculpting – A/B testing for UX and conversion – Voice search optimization – Content refresh for freshness signals | – Digital PR for high-authority backlinks – Podcast guesting or interviews – HARO (Help A Reporter Out) link building – Influencer collaborations – Strategic partnerships for co-content marketing |
Example:
A company updating its product pages for structured data (On-Site) can also publish expert guest articles on authority blogs (Off-Site) — combining both drives maximum results.
How On-Site and Off-Site SEO Work Together
Search engine algorithms reward websites that show balance — quality content (On-Site) supported by trust signals (Off-Site).
- On-Site SEO ensures your site is discoverable, understandable, and user-friendly.
- Off-Site SEO ensures your site is trusted, recommended, and referenced.
When both are executed consistently, your rankings grow steadily and sustainably.
Summary Table: On-Site SEO vs Off-Site SEO
| Category | On-Site SEO | Off-Site SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Internal website optimization | External reputation building |
| Main Focus | Keywords, structure, content, speed | Links, mentions, partnerships |
| Objective | Improve user experience & visibility | Build authority & trust |
| Responsibility | Website owner & SEO team | Marketing, PR, community efforts |
| Timeframe for Results | Short to medium term | Medium to long term |
| Control | Direct control | Indirect influence |
| Outcome | Higher relevance & usability | Higher domain authority & credibility |

On-Site SEO and Off-Site SEO are not competitors — they’re collaborators in your digital growth story.
- Without On-Site SEO, search engines won’t understand your value.
- Without Off-Site SEO, they won’t believe in your credibility.
By mastering both, you create a website that’s clear, trustworthy, and authoritative — one that ranks high, earns clicks, and wins loyal customers.
Advanced On-Site SEO Tactics
Once the basics are in place, advanced strategies can take your optimization to the next level.
1. Semantic Keyword Integration (LSI)
Google now understands meaning, not just words. Include related terms that add depth and context — this boosts topic authority.
Imagine writing about “On-Site SEO” and only repeating that phrase endlessly — it sounds robotic, right? That’s where Semantic Keyword Integration (LSI) steps in. Instead of overusing one keyword, you enrich your content with related terms that give context and depth. For example, if your main keyword is On-Site SEO, include natural variations like meta tags, keyword placement, content optimization, and page speed. Search engines now understand meaning, not just words. By weaving these related ideas naturally into your story, you make content feel more human — and help Google see it as more relevant, complete, and trustworthy. See the image for more understanding about it.
2. Schema Markup for Rich Results
Adding structured data helps search engines display enhanced snippets (ratings, FAQs, etc.), increasing click-through rates.
3. Content Freshness
Update key pages regularly with new data, examples, and visuals. Freshness signals relevance.
4. Internal Link Sculpting
Use internal links strategically to pass authority to cornerstone pages. Keep link count balanced and contextually relevant.
5. Voice Search Optimization
Optimize for conversational queries (“How to improve On-Site SEO?”) to capture voice-based search traffic.
6. Entity-Based Optimization
Align your content with recognized entities (brands, concepts, topics) using schema and semantic cues — it helps Google associate your pages with specific subject expertise.
7. Data-Driven Refinement
Analyze heatmaps, session durations, and click patterns to identify improvement areas. Experiment with A/B testing headlines, CTAs, and layouts.
Each tactic enhances your website’s ability to communicate relevance and trust — the two currencies of modern SEO.
Key Takeaways
- On-Site SEO is the foundation of visibility. Without it, no amount of backlinks or ads can sustain rankings.
- User intent drives optimization. Write for people first, then fine-tune for search engines.
- Consistency matters. Optimization is an ongoing process — small updates compound over time.
- Balance On-Site with Technical and Off-Site SEO. They’re interconnected, not isolated.
- Track, measure, and improve. Use analytics to refine your SEO strategy continuously.
Your website isn’t just a collection of pages; it’s your brand’s digital ecosystem. Each word, tag, and link tells search engines how relevant and reliable you are. When you master On-Site SEO, you don’t just rank higher — you build a stronger, smarter online presence that works around the clock to attract and convert the right audience.


