Every successful company shares one common principle — a commitment to innovation through effective product development. As discussed in core business growth strategies, product development is not just a department-level activity; it’s a core business function that drives long-term growth, brand relevance, and customer satisfaction. It determines how well a business can adapt to market changes, respond to evolving consumer needs, and create lasting value in competitive industries.
Developing new products or improving existing ones helps businesses expand into new markets, strengthen brand positioning, and maintain a steady flow of innovation. It’s the process that transforms ideas into solutions customers truly need — and when aligned with broader growth strategies, it becomes a powerful engine for profitability and sustainability.
What Is Product Development?
Product development is the structured process of conceptualizing, designing, testing, and launching new or improved products that solve specific customer problems. It’s not limited to manufacturing or design — it combines market research in product development, strategy, innovation, and execution to deliver products that align with business goals.
Its importance lies in its ability to connect business vision with market demand. When companies continuously refine or introduce products that match customer expectations, they strengthen their market presence and future-proof their brand. Businesses that neglect this process often stagnate, while those that prioritize it consistently lead their industries.
For instance, smartphone brands like Samsung and Apple invest heavily in R&D, ensuring each new launch not only upgrades technology but also improves user experience. These companies understand that innovation isn’t an option — it’s a necessity for sustained growth.
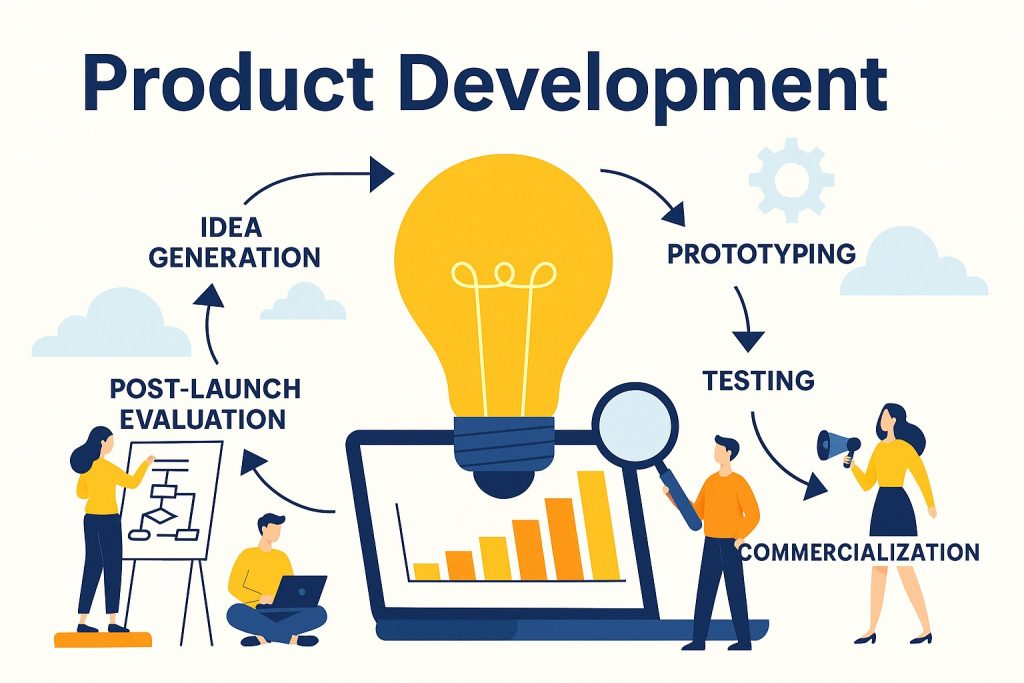
7 Key Stages of Product Development
Effective product development follows a series of stages that guide an idea from inception to launch. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the product meets both market expectations and business objectives.
1. Idea Generation
Every great product starts with an idea. Businesses can gather ideas through customer feedback, market trends, employee suggestions, and competitor analysis. The goal is to identify gaps in the market and find ways to address them creatively.
Tips: Keep an open channel for feedback — your customers are often the best source of new ideas to read blogs.
2. Idea Screening
Once you have several ideas, filter them based on feasibility, cost, and market potential. Not every idea is worth pursuing, so objective evaluation prevents wasted effort and resources.
Challenge: Avoid emotional bias — focus on the data, not personal preferences.
3. Concept Development and Testing
A promising idea now becomes a detailed concept. Define your target audience, pricing strategy, design, and value proposition. Test the concept with focus groups or online surveys to validate demand before investing further.
Example: A sanitaryware brand might test design prototypes with architects and homeowners before finalizing a new basin model.
4. Product Design and Prototyping
This is where the idea takes form. Engineers, designers, and marketers collaborate to create a prototype that demonstrates the product’s features and benefits. Early prototypes allow rapid feedback and improvement.
Tip: Use digital tools like CAD and 3D modeling to visualize and refine designs efficiently.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Before a full-scale launch, the product must be tested for performance, safety, usability, and customer satisfaction. Quality assurance ensures your product delivers what it promises.
Mistake to Avoid: Rushing to market without sufficient testing often leads to recalls or brand damage.
6. Commercialization and Market Launch
A product is only as successful as its launch strategy. At this stage, marketing, sales, logistics, and customer support must work in sync. A strong marketing campaign, aligned with your overall business objectives, ensures awareness and adoption. To maximize results, link your launch plan to your broader growth framework — as highlighted in Business Growth Strategies — ensuring that your product rollout supports revenue expansion and brand development goals.
7. Post-Launch Evaluation and Improvement
After launch, a product’s true success depends on how effectively it performs in the market. This stage focuses on monitoring key metrics such as sales, customer feedback, and satisfaction levels. Real user insights reveal opportunities to refine features, packaging, or pricing for better results. Many leading brands continuously improve their products through updates and redesigns to stay competitive. This ongoing process not only enhances quality but also strengthens market visibility—an essential step in building brand awareness. By applying customer feedback strategically, each improvement adds long-term value, boosts loyalty, and drives sustainable business growth.
Example: Software companies release updates regularly to enhance performance and fix bugs based on user insights.
Aligning Product Development with Business Growth
Product development should never operate in isolation. It must be strategically integrated with your company’s growth objectives — from market penetration to diversification. For instance, introducing an upgraded version of an existing product can help deepen customer engagement (market penetration), while launching an entirely new line can open doors to new audiences (market development).
Aligning product innovation with organizational goals ensures every effort contributes to measurable outcomes such as higher sales, brand equity, and operational efficiency. When guided by the principles of Business Growth, businesses can channel product development toward targeted results — ensuring that creativity translates into commercial success.
Modern Trends Shaping Product Development
The product development landscape is evolving faster than ever. Modern consumers expect more personalization, sustainability, and technological sophistication. Businesses that embrace these trends gain a competitive edge and build deeper customer trust.
- Sustainability and Eco-Design
Eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient processes, and waste reduction are becoming essential. Sustainable products appeal to conscious consumers and enhance brand reputation. - AI and Data-Driven Innovation
Artificial intelligence and analytics help businesses understand customer preferences and predict demand. Data-driven decisions lead to better designs and faster iterations. - Digital Transformation
Smart technologies, IoT integration, and cloud-based collaboration tools accelerate product development cycles and improve quality control. - Customer Co-Creation
Inviting customers into the design process ensures real-world relevance. Co-creation builds stronger emotional connections and higher satisfaction. - Agile and Lean Methodologies
Modern teams use agile frameworks to shorten development time and reduce costs. Lean product management encourages testing small, learning fast, and scaling effectively.
Each of these trends reinforces the growth mindset emphasized in Business Growth Strategies, helping businesses stay adaptable and future-ready in fast-moving industries.
Common Challenges in Product Development
While rewarding, the product development journey comes with its challenges. Recognizing them early can save significant time and cost.
- High Development Costs: Research, testing, and materials can be expensive. Start small, validate early, and scale once results are proven.
- Unclear Customer Needs: Poor market understanding can derail even the best ideas. Use data analytics, surveys, and user testing to stay aligned with customer expectations.
- Time-to-Market Delays: Complex approval processes and poor coordination cause delays. Implement agile project management to speed up workflows.
- Cross-Team Misalignment: Development, marketing, and sales must share the same vision. Encourage regular cross-department meetings and unified KPIs.
- Quality Risks: Cutting corners in testing often leads to long-term reputation damage. Prioritize quality, even if it slightly extends timelines.
Case Example: A American ceramic manufacturer developed a new water-efficient toilet line after conducting feedback sessions with builders and customers. By using lean methods and continuous testing, the brand launched a high-demand product within budget — increasing both market share and sustainability reputation.
Innovation as the Heart of Growth
Product development isn’t just a process — it’s the strategic foundation of business growth. It’s how organizations evolve, attract new markets, and maintain customer loyalty. Every improvement, feature update, or new design is a step toward greater competitiveness and profitability.
When executed with clarity and alignment, product development bridges innovation with purpose. It empowers businesses to scale sustainably and respond quickly to changing customer expectations.
The formula is clear: build smart, test fast, improve continuously — and your products will drive the growth your business deserves.

