You’ve built a beautiful website. You’ve poured hours into crafting the perfect copy.
You’ve even invested time in keyword planning for content, targeting high-volume keywords that should be bringing in traffic.
But when you check your analytics? Crickets.
You’re not alone. In fact, a staggering 90.63% of content gets zero traffic from Google. Zero.
Why? Because ranking on the first page isn’t enough anymore. Being at position #9 is basically the same as being invisible. If you want real traffic, the kind that converts into sales and revenue and you don’t just need SEO. You need Search Engine Positioning.

Search Engine Positioning is the difference between showing up to the party and being the life of it. It’s the strategic art of not just ranking, but dominating the specific spots on the SERP (Search Engine Results Page) that actually drive clicks.
In this guide, we’re going to tear down the old-school “just publish and pray” mentality. We’re going to dive deep into how algorithms actually evaluate your position, the advanced frameworks experts use to climb the ladder, and the actionable steps you can take right now to own the top spots.
Let’s dive in.
What is Search Engine Positioning?
Let’s clear up a common misconception right off the bat.
Most people use “SEO” and “Search Engine Positioning” interchangeably. They aren’t the same thing.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the broad practice of improving your site’s visibility. It includes technical fixes, site speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall content strategy. Think of SEO as the foundation of a house. You need it so the structure doesn’t collapse.
Search Engine Positioning is the interior design of the penthouse suite. It is a subset of SEO focused specifically on maximizing the ranking of individual pages for specific keywords to achieve the highest possible position on the SERP.
It’s not just about “ranking.” It’s about ranking optimization.
When we talk about positioning, we aren’t just aiming for the top 10. We are aiming for the top 3. Or even better, “Position Zero” that coveted Featured Snippet box that steals all the attention before a user even scrolls.
Why the distinction? Because you can have great “SEO health” (no broken links, fast load times) and still have terrible positioning (ranking #12 for your main money keyword).
Positioning is the tactical execution of getting a specific URL from page 2 to the top of page 1.
Why is Search Engine Positioning Important?
If you take one thing away from this article, make it this: The winner takes it all.
We aren’t just saying that to be dramatic. The data backs it up.
According to extensive studies by Backlinko and Sistrix, the click-through rate (CTR) drops off a cliff the further down you go on page 1.
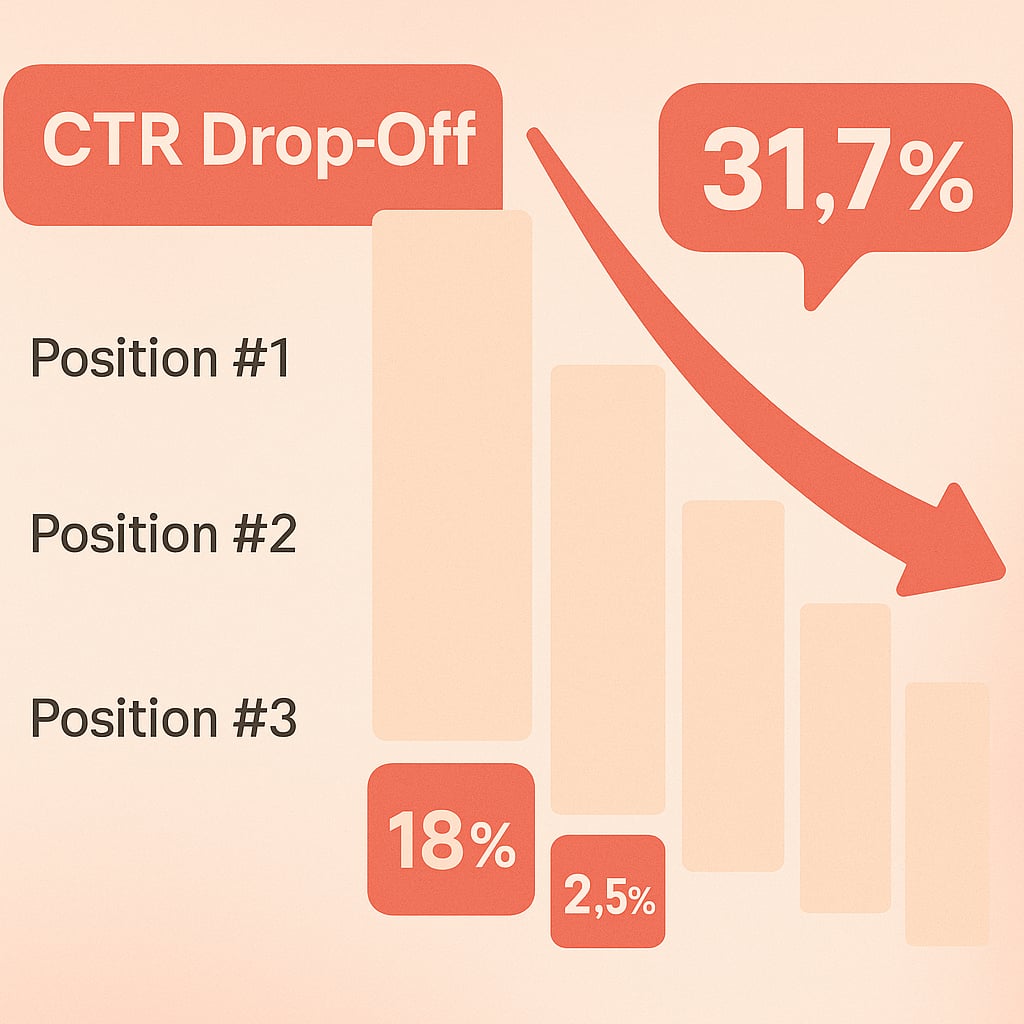
- Position #1 receives approximately 31.7% of all clicks.
- Position #2 gets about 24%.
- Position #3 drops to around 18%.
- Position #10? You’re looking at a measly 2.5%.
Let’s do the math.
Imagine you are ranking for a keyword that gets 10,000 searches a month.
If you are in Position #10, you are getting roughly 250 visitors.
If you move that same page to Position #1, you are suddenly getting 3,170 visitors.
That is a 1,168% increase in traffic without creating a single new piece of content. You didn’t write a new blog post. You didn’t launch a new product. You just improved your positioning.
But it’s not just about raw traffic numbers. It’s about authority.
When users search for a solution to their problem, whether it’s “best CRM for startups” or “how to fix a leaky faucet”—they instinctively trust the top results. High positioning signals to the user (and to competitors) that you are the market leader. It builds brand equity that paid ads simply cannot buy.
Search Engine Positioning vs. SEO
We touched on this earlier, but it’s crucial to understand the nuance.
SEO is the war. Positioning is the battle.
SEO is a long-term, holistic strategy. It involves:
- Site architecture
- URL structure
- Sitemaps
- Overall domain authority
Search Engine Positioning is a surgical strike. It involves:
- Optimizing a specific page’s H1 and title tags.
- Updating the content on that page to be more relevant than the current #1 result.
- Building internal links specifically to that URL.
- Optimizing for CTR (Click-Through Rate) to signal relevance to Google.
You can have excellent SEO and poor positioning. Conversely, you can have a site with average technical SEO that still dominates positioning for a few specific, high-value keywords because the content is undeniable.
How Algorithms Evaluate Positions
If you want to beat the algorithm, you have to think like the algorithm.
Google’s ranking algorithm isn’t a person deciding which websites are “cool.” It’s a complex mathematical equation with over 200 ranking factors. However, for positioning specifically, the algorithm cares about three core pillars: Relevance, Authority, and User Experience signals.
1. Relevance (The “Inverted Index”)
When a user types a query, Google scans its massive index to find pages that contain the same keywords. But it goes deeper than that. It uses Semantic Search.
Google doesn’t just look for the string of characters “best running shoes.” It looks for the intent behind it. It looks for related terms like “durability,” “marathon,” “cushioning,” and “arch support.”
If your page mentions the keyword once but fails to cover the topic comprehensively (Semantic Relevance), your positioning will suffer.
2. Authority (PageRank)
Yes, PageRank still matters. This is the vote of confidence from other websites. If high-authority sites in your niche link to your specific page, Google views that page as a trusted resource.
However, for positioning, internal links are often the secret weapon. By linking from your high-authority homepage to a specific blog post, you pass “link juice” that can bump that post’s position significantly.
3. User Experience Signals (RankBrain)
This is the game-changer. Google uses machine learning (RankBrain) to watch how users interact with the search results.
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): If you rank #5 but more people click your title than the guy at #3, Google notices. It thinks, “Hey, this result must be more relevant,” and eventually swaps your positions.
- Dwell Time: If users click your link and immediately hit the “Back” button (Pogo-sticking), it tells Google your content didn’t answer the query. Your position drops.
- Long Clicks: If users stay on your page for minutes, scroll down, and read? That’s a “Long Click.” It’s pure gold for positioning.
Key Ranking Factors for Positioning
So, what levers can you actually pull? While there are hundreds of factors, these are the ones that move the needle for positioning specifically.
Content Depth and “Freshness”
Google loves fresh content. If you wrote a guide in 2018 and haven’t touched it since, you’re likely losing position to a competitor who updated their guide last week.
But it’s not just about the date. It’s about Content Depth. Does your page answer the user’s question so thoroughly that they don’t need to go back to Google? That is the ultimate goal.
The “Skyscraper” Factor
This is a classic Brian Dean strategy. Look at the content currently ranking #1. Now, ask yourself: How can I make my page 10x better?
- Is their guide 1,000 words? Make yours 3,000.
- Do they use stock photos? Use custom infographics.
- Is their data from 2021? Update yours with 2024 statistics.
Core Web Vitals
Google has explicitly stated that Core Web Vitals (loading, interactivity, visual stability) are ranking factors. If your page takes 5 seconds to load, users bounce. If users bounce, your position tanks. It’s that simple.
Mobile-First Indexing
Google predominantly uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking. If your desktop site looks great but your mobile site is a mess of pop-ups and unreadable text, your positioning is doomed.
Advanced Optimization Frameworks
Ready to get your hands dirty? Here are three advanced frameworks to skyrocket your positioning.
1. The “Keyword Gap” Strategy
Most people optimize for the keywords they think they want. The pros optimize for the keywords their competitors are already ranking for.
Use a tool like Semrush or Ahrefs. Plug in your competitor’s URL. See exactly which keywords are driving their traffic. Now, look for the “Gap”—keywords they rank for that you don’t. Create dedicated pages for those keywords, but make your content superior.
2. The Semantic Content Network
Don’t just write one lonely article about a topic. Create a Topic Cluster.
- Pillar Page: A massive, 3,000-word guide covering a broad topic (e.g., “Digital Marketing”).
- Cluster Pages: Smaller articles covering sub-topics (e.g., “Email Marketing Tips,” “SEO Basics,” “PPC Guide”).
Link all the Cluster Pages back to the Pillar Page. This tells Google, “We are the ultimate authority on this entire topic.” It lifts the positioning of every page in the cluster.
3. SERP Feature Sniping
Remember Position Zero? That little box at the top with the answer? You can steal it.
Google usually pulls Featured Snippets from pages already ranking on Page 1. To capture it:
- Identify a question-based keyword (e.g., “how to tie a tie”).
- Look at the current snippet. Is it a list? A paragraph? A table?
- Format your content to match that structure perfectly.
- Place the question in an H2 tag, and answer it immediately and concisely (40-60 words) directly below.
Real Case Studies: Positioning in Action
Let’s look at how this works in the real world.
Case Study A: The “Old Blog Post” Revival
A SaaS company had a blog post about “Project Management Tips” stuck at Position #8. It was getting about 100 visits a month.
The Strategy:
- Updated the Content: They added a new section on “Remote Project Management” (relevant to current trends).
- Improved CTR: They changed the title from “10 Project Management Tips” to “10 Project Management Tips for 2024 (Expert Guide).”
- Internal Linking: They added links to this post from their 5 most popular blog posts.
The Result:
Within 3 weeks, the post jumped to Position #2. Traffic increased to 1,500 visits a month.
Case Study B: The Featured Snippet Heist
An e-commerce store sold specialized coffee equipment. They ranked #4 for “how to clean a french press.”
The Strategy:
They noticed the Featured Snippet was a numbered list from a competitor. They edited their article to include a clear, bolded H2: “How to Clean a French Press in 5 Steps” and followed it with a concise numbered list.
The Result:
Google awarded them the Featured Snippet (Position Zero). Their CTR jumped from 6% to 28% overnight, surpassing the #1 organic result.
Strategic Checklist for Domination
If you want to improve your search engine positioning today, follow this checklist:
- Audit Your “Striking Distance” Keywords: Go to Google Search Console. Filter for keywords ranking between Position #4 and #20. These are your low-hanging fruit. Prioritize these pages.
- Analyze the Search Intent: Look at the top 3 results for your target keyword. Are they blog posts? Product pages? Videos? Ensure your page type matches what Google wants to show.
- Optimize for CTR: Write magnetic Title Tags and Meta Descriptions. Use power words, numbers, and brackets. (e.g., “The Ultimate Guide [2024 Update]”).
- Boost Page Speed: Run your page through Google PageSpeed Insights. Fix anything red.
- Build Internal Links: Find your site’s most powerful pages and link from them to the page you want to boost.
- Update Content: Add new data, new examples, and new media. Make it fresh.
Actionable Steps for Long-Term Visibility
Positioning isn’t a “set it and forget it” task. It’s a war of attrition.
Monitor Your Rankings Weekly.
Use a rank tracker. If you see a drop, investigate immediately. Did a competitor update their page? Did search intent change?
Spy on Your Competitors.
Set up alerts for when your competitors publish new content. If they are targeting your keywords, go back to your page and make it better.
Focus on User Satisfaction.
At the end of the day, Google wants to make users happy. If your content solves the user’s problem faster and better than anyone else, the algorithm will reward you.
Dominating the SERPs isn’t magic. It’s a mix of psychology, technology, and relentless execution. Start with your striking distance keywords, optimize for the user, and watch your positioning climb.

