Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is one of the most powerful digital marketing strategies for anyone who wants to succeed online. Whether you are a student running a personal blog, a small café looking to attract local customers, or a global enterprise aiming for international visibility, SEO determines how easily people can find you on Google, Bing, or even YouTube.

In the early 2000s, SEO was often reduced to keyword stuffing and link farms. Businesses tried to game the system by cramming keywords into web pages or buying low-quality backlinks. But search engines evolved. Today, SEO is no longer about tricks; it’s about creating useful, relevant, and user-friendly experiences. With artificial intelligence, machine learning, and user-intent analysis shaping search, SEO has become a blend of technical expertise, content creation with good strategies, and user experience optimization.
Despite myths claiming “SEO is dead,” it is alive and thriving. The businesses that invest in SEO are the ones that secure long-term visibility, authority, and customer trust. This guide explores SEO from the ground up, showing you exactly how it works, why it matters, and how to implement it for lasting success.
What is SEO?
At its core, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of improving a website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). When someone searches for a product, service, or information, search engines like Google crawl billions of web pages and rank them based on relevance, authority, and user experience.
For businesses, this means that ranking higher for relevant search terms directly translates into more traffic, leads, and sales. For example:
- An e-commerce store selling fashion products can attract customers searching for “affordable men’s jackets.”
- A blogger who optimizes content for “best travel tips in Europe” can generate traffic and ad revenue.
- A plumber in Newyork ranking for “emergency plumber near me” can secure valuable service calls.
SEO is not limited to big companies; it works for individuals, startups, and local businesses. In fact, for entrepreneurs who want to Start a New Business, SEO can be the most cost-effective way to build visibility without heavy advertising costs.
What is the Difference Between SEO, SEM, and PPC?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
SEO focuses on organic rankings. It doesn’t involve direct payment to search engines but requires time, effort, and strategy. The goal is to optimize content, technical aspects, and authority to appear naturally in search results.
Pros: Cost-effective, builds long-term credibility, sustainable traffic.
Cons: Takes time, requires ongoing effort.
SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
SEM is the umbrella term that includes both organic SEO and paid search advertising. It involves optimizing your website and running ads to appear at the top of search results.

Search engine marketing examples
Pros: Offers flexibility, combines organic growth with paid visibility.
Cons: Requires a balanced budget and expertise to manage.
PPC (Pay-Per-Click)
PPC refers specifically to paid ads where businesses pay for every click. Platforms like Google Ads and Bing Ads allow businesses to target specific keywords and audiences.

Pros: Instant visibility, measurable ROI, precise targeting.
Cons: Can be expensive, traffic stops once ads are turned off.
Example in Action:
- A startup blogger may rely on SEO to build organic visibility.
- A retail brand launching a new collection may use PPC for immediate results.
- A large corporation often uses SEM to balance both.
In short, SEO is the long game, PPC is the quick win, and SEM combines both for growth.
Why SEO is So Important?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is more than just a digital marketing tactic — it’s the foundation of online visibility and credibility in the modern world. Every second, millions of searches happen on Google, Bing, and other platforms. If your business doesn’t appear where your customers are searching, you’re essentially invisible. Let’s explore in detail why SEO is absolutely vital for individuals, small businesses, and enterprises.
1. Visibility and Traffic
The higher your website ranks in search engine results, the more likely people are to click on it. Research shows that over 90% of clicks go to results on the first page of Google, with the top three results capturing the lion’s share.
For example:
- A small online boutique ranking on the first page for “affordable women’s dresses in Dhaka” will attract a steady flow of customers without spending heavily on ads.
- A local doctor’s clinic appearing in the top results for “best pediatrician near me” will consistently gain new patients.
Without SEO, your site could end up buried on page three or four, where almost no one looks. SEO ensures your brand is discoverable where people are searching.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to traditional advertising or Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaigns, SEO is one of the most cost-effective strategies. Once your site ranks for a keyword, you don’t pay for each visitor — the traffic is free and ongoing.
Think about it like this:
- PPC is like renting a billboard. You pay as long as it’s up. Once you stop paying, visibility vanishes.
- SEO is like owning a storefront in a busy market. Once established, customers keep walking in without additional cost.
3. Trust and Credibility
Users generally trust organic results more than paid ads. When people see your website ranking naturally in the top results, they perceive your brand as authoritative, reliable, and trustworthy.
For instance:
- A financial blog ranking on the first page for “how to save for retirement” will gain credibility among readers compared to a random ad.
- A restaurant with strong SEO and consistent reviews in Google’s local pack appears more authentic than one only relying on paid promotions.
Search engines are like digital referees — if you show up at the top, users believe you’ve “earned your place.” This credibility is priceless.
4. Higher ROI (Return on Investment)
SEO may take time to show results, but its long-term ROI far outpaces many other marketing channels. Unlike ads, which stop working when you stop paying, SEO continues to generate results even months or years later.
Example:
- A blogger investing in content SEO may spend hours writing a guide today, but that same article can attract traffic for years with minor updates.
- An e-commerce store optimizing product pages can continuously drive conversions without spending extra on ads.
When combined with good analytics and Market Research, SEO helps you understand customer behavior and refine strategies for maximum ROI.
5. Long-Term Growth
SEO is not a one-time project — it’s an ongoing investment that grows with your business. Unlike temporary campaigns, SEO builds a foundation for sustainable success.
Consider this:
- A well-optimized blog that consistently publishes useful content will steadily increase traffic, authority, and revenue.
- A tech company investing in SEO-friendly product pages will continuously attract potential customers, even as competitors come and go.
For entrepreneurs creating a long-term Business Plan, SEO should be included as a core growth strategy because it creates a compounding effect. The more optimized content you publish, the stronger your digital presence becomes.
What This Graph Tells Us About the Power of SEO

Image of my website
The image above represents real performance data from a website’s Google Search Console, showing how search engine optimization (SEO) directly impacts visibility and traffic over time.
- Total Clicks (37.1K) – This is the number of times people actually clicked your website link on Google. Every click represents a real visitor, potential lead, or customer.
- Total Impressions (166K) – This shows how often your site appeared in Google search results. The more impressions you have, the more people are discovering your brand organically.
- Average CTR (22.4%) – CTR (Click-Through Rate) measures how attractive your listings are. A 22.4% CTR is remarkably high, proving that well-optimized titles and meta descriptions convince users to click.
- Average Position (10) – Ranking within the top 10 means your content is appearing on the first page of Google, which is where 90% of users stop their search.
This chart visualizes how consistent SEO efforts — keyword optimization, content updates, and link-building — generate long-term, compounding growth. Notice how the clicks (blue line) and impressions (purple line) rise and fluctuate together:
- When impressions increase, it means your pages are being shown for more keywords.
- When clicks increase, it proves users find your content relevant and trustworthy.
Unlike paid ads that stop delivering once your budget ends, SEO builds sustainable visibility. Every blog post, keyword, and backlink adds to your online authority — and that authority keeps attracting traffic even while you sleep.
Types of SEO Optimization
SEO is a broad discipline, but at its core, it can be divided into three main areas: Technical SEO, On-Site SEO, and Off-Site SEO. Each plays a critical role in helping websites perform well in search engine rankings, attract the right audience, and build long-term digital authority.
- Technical SEO: Optimizing the Technical Aspects of a Website
- On-Site SEO: Optimizing Content for Users and Search Engines
- Off-Site SEO: Building Authority and Brand Recognition
Technical SEO: Optimizing the Technical Aspects of a Website
Technical SEO refers to optimizing the infrastructure of a website so that search engines can crawl, index, and rank it efficiently. While content attracts users, technical SEO ensures that the website is search engine-friendly at its foundation. Without proper technical setup, even the best content might remain invisible to Google and other search engines.

Key Elements of Technical SEO:
- Site Architecture: A well-structured website with logical navigation ensures that both users and crawlers can find content easily. For example, using a silo structure (categories → subcategories → pages) improves crawlability.
- XML Sitemaps & Robots.txt: Submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console helps crawlers understand which pages are important. A properly configured robots.txt file prevents indexing of irrelevant or duplicate pages.
- Mobile-First Indexing: Since Google now primarily uses the mobile version of a site for ranking, responsive design and mobile optimization are non-negotiable.
- Site Speed & Core Web Vitals: Fast-loading pages improve user experience and rankings. Core Web Vitals measure loading (LCP), interactivity (FID/INP), and visual stability (CLS).

- HTTPS Security: Websites with SSL certificates (HTTPS) are favored by search engines and provide users with trust and safety.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): Adding schema helps search engines better interpret your content (e.g., product reviews, FAQs, recipes).
- Canonicalization & Duplicate Content Control: Canonical tags tell Google which version of a page is the “master,” preventing duplicate content issues.
Example of Technical SEO in Action:
Imagine an e-commerce store with 10,000 product pages. Without a proper sitemap, Google may not crawl all pages, leaving many products invisible in search. By implementing structured sitemaps, compressing images, and fixing crawl errors, the store can ensure every page is discoverable — directly increasing organic traffic and sales.
Takeaway: Technical SEO lays the foundation. Think of it as building a strong digital house — without it, everything else collapses.
2. On-Site SEO: Optimizing Content for Users and Search Engines
On-site SEO (also called On-Page SEO) focuses on optimizing the content and elements within your website to make it more relevant, engaging, and discoverable by search engines. It’s about ensuring that every page answers the user’s query while also signaling relevance to search engines.

Key Elements of On-Site SEO:
- Keyword Optimization: Using the right mix of primary, secondary, and semantic keywords within content, titles, headers, and meta descriptions. For example, instead of stuffing “buy ceramic basin online,” also use related terms like “affordable washbasin in United States” to capture wider search intent.
- Meta Tags: Well-crafted title tags and meta descriptions improve click-through rates (CTR). They act as an “advertisement” in search results.
- Header Tags (H1–H6): Proper heading structure improves readability and signals content hierarchy to search engines.
- Internal Linking: Connecting related pages (e.g., linking an article on SEO basics to Market Research or Business Plan guides users deeper into the site and distributes link equity.

- Content Relevance & Depth: Google favors long-form, well-researched, original content that comprehensively covers a topic.
- Image Optimization: Using descriptive alt text, optimized file sizes, and relevant file names improves both SEO and accessibility.
- User Experience (UX): Readability, page design, and navigation are part of SEO. A site that is easy to read and navigate keeps users engaged longer.
- Content Freshness: Updating old posts with new data, images, or stats keeps content relevant.
Example of On-Site SEO in Action:
A blog post about “Digital Marketing Trends in 2025” may rank poorly if it only has a few short paragraphs. By expanding it to cover AI, influencer marketing, voice search, and case studies, adding optimized images, and linking to related posts like “Future of AI in Digital Marketing,” the post becomes more authoritative and user-friendly, helping it climb in rankings.
Takeaway: On-site SEO makes sure that the content you produce is not just good but optimized to compete in search results
3. Off-Site SEO: Building Authority and Brand Recognition
Off-site SEO (often called Off-Page SEO) refers to actions taken outside your website that influence its rankings and authority. While technical and on-site SEO make your website strong, off-site SEO signals to search engines that your site is trusted and valued by others.

But it’s more than just backlinks. Modern off-site SEO includes brand building, digital PR strategies, and demand generation.
Key Elements of Off-Site SEO:
- Backlinks: Quality links from authoritative websites remain a major ranking factor. A backlink from Forbes is far more powerful than ten links from unknown blogs. Free high quality backlinks also can help you to build authorities like wordpress.com, medium.com, tumblr.com and many more web 2.0s.
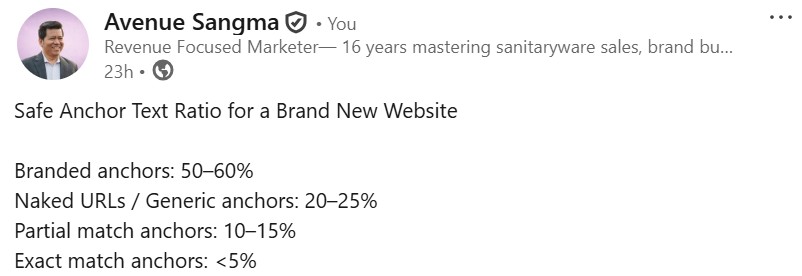
- Anchor Text: in Off-Page SEO is the clickable word in backlinks. Using relevant, natural keywords improves search rankings, context, and trust while avoiding over-optimization to prevent penalties.
- Best Practices of Anchor Texts are – Use a Natural Mix and These are –
- Exact match (your keyword) – limited use.
- Partial match (variation of keyword).
- Branded anchors (your brand name).
- Generic anchors (learn more, read here).
- Naked URLs (https://example.com).
- Best Practices of Anchor Texts are – Use a Natural Mix and These are –
Safe Anchor Text Ratio Image
- Brand Mentions: Even unlinked mentions of your brand (e.g., people talking about “Charu Ceramic” on social media) contribute to trust signals.
- Digital PR: Publishing guest posts, being featured in news outlets, and collaborating with influencers enhance brand reach and SEO.
- Social Signals: While not a direct ranking factor, social engagement (shares, likes, comments) drives traffic and builds visibility.
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Search engines reward brands that demonstrate thought leadership, expertise, and consistency across the web.
- Reputation Management: Positive reviews on platforms like Google Business Profile, Trustpilot, or industry-specific directories build credibility.
- Brand Assets: Building consistent brand identity — logos, slogans, colors, catchphrases, and values — makes your brand recognizable and memorable.
Example of Off-Site SEO in Action:
Suppose a startup launches a health blog. Publishing content is not enough. By contributing guest articles on health websites, securing mentions from nutrition influencers, and earning backlinks from academic studies, the site builds authority. Over time, Google sees it as a trusted voice in the health niche, boosting rankings.
Takeaway: Off-site SEO is about reputation. Think of it as word of mouth in the digital world — the more trusted voices mention you, the stronger your brand and rankings become.
SEO in the Digital World
SEO is like a three-legged stool: Technical SEO provides stability, On-Site SEO creates relevance, and Off-Site SEO builds authority. Neglecting any one of these can weaken your digital presence.
- Without technical SEO, search engines may never find or index your site.
- Without on-site SEO, your content won’t align with search intent.
- Without off-site SEO, your site won’t gain the trust it needs to rank competitively.
When combined, these three types of optimization ensure that your website is technically sound, content-rich, and widely trusted — the ultimate recipe for long-term search engine success.
Optimize Your Website: A Practical Guide
Optimizing your website is one of the most effective ways to improve visibility, attract organic traffic, and deliver a better user experience. A well-optimized site not only ranks higher in search engines but also keeps visitors engaged and encourages them to take action. Below are the essential steps to follow:
1. Conduct Keyword Research
The foundation of SEO begins with understanding what your audience is searching for with a great keyword research strategy. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to identify high-traffic, low-competition keywords. Focus on long-tail keywords that align with your products, services, or blog topics.
2. Ensure Mobile Responsiveness
With most searches happening on smartphones, your website must adapt seamlessly to different devices. A responsive design improves usability and helps your site perform better under Google’s mobile-first indexing.
3. Use Internal Linking
Strategically linking related articles or product pages helps search engines crawl your site more effectively and keeps users exploring longer — improving both SEO and user experience. For instance, when you connect a post about SEO basics to a detailed Internal Linking guide or a comprehensive Market Research article, readers naturally move deeper into your content ecosystem. This not only increases dwell time but also strengthens the contextual relevance of your pages, signaling to search engines that your site offers valuable, interconnected information.
4. Publish and Update Fresh Content
Outdated information can hurt rankings. Regularly update old blog posts with new data and publish fresh, original content that solves user problems.
5. Add Schema Markup
Structured data helps search engines understand your content better, enabling features like rich snippets in search results. For instance, recipe schema can display cooking times or reviews.
6. Improve Page Speed
Slow websites frustrate users and lower rankings. Compress images, use browser caching, and consider a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to improve loading times.
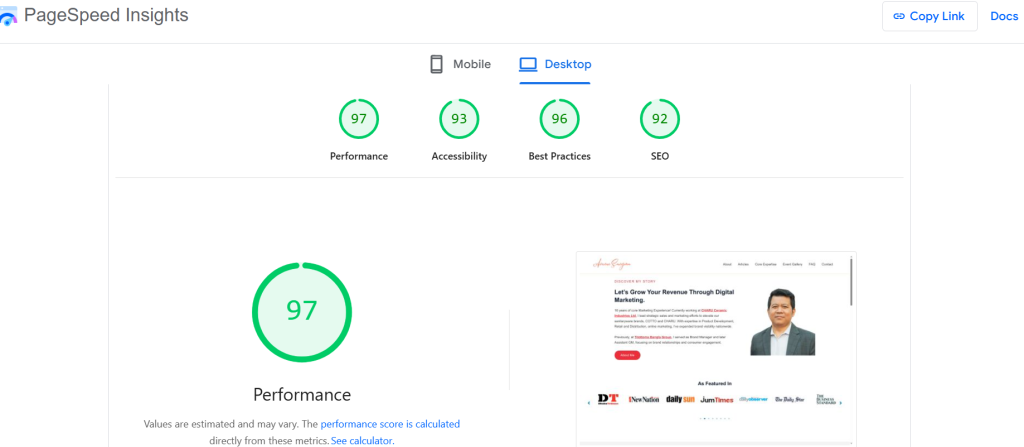
Desktop PageSpeed Insights
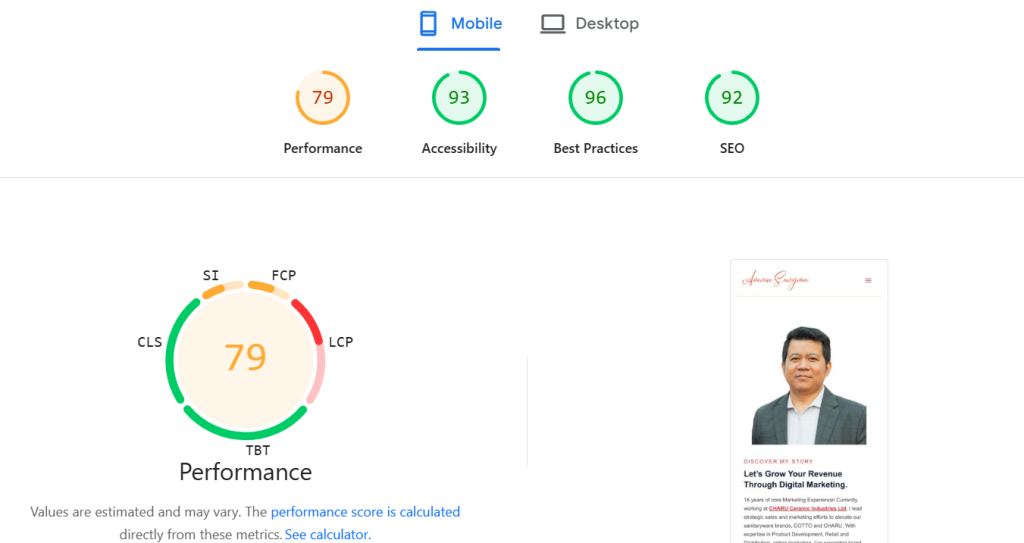
Mobile PageSpeed Insights
When combined with a strong Business Plan, these steps ensure your website is built for both immediate visibility and long-term growth.
Why Google Prioritizes Interesting and Useful Websites?
Google’s mission has always been to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” To achieve this, its algorithms are designed to reward websites that genuinely help users. When visitors find a site interesting, they spend more time engaging with content, click through multiple pages, and are more likely to return. These positive signals — known as user engagement metrics — tell Google that the site is delivering real value.
For example, a blog post filled with compelling case studies, clear explanations, and visuals reduces bounce rates because readers don’t quickly leave the page. Similarly, an e-commerce store offering detailed product descriptions, customer reviews, and demo videos builds trust and encourages purchases.
Google also looks at E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness).
Sites that demonstrate expertise and create helpful, original content stand out from competitors using generic or low-value information. By prioritizing useful and engaging sites, Google ensures users get the best possible answers — whether they’re looking for health tips, financial advice, or product recommendations.
In short, interesting and useful websites keep users satisfied, and Google rewards them with higher rankings because happy users equal a stronger search ecosystem.
Understand How Search Engines Work
Search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo are designed to help people find information quickly and accurately. Behind the scenes, they use advanced algorithms, but the process can be broken down into three key steps:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Ranking
1. Crawling
Search engines send out automated bots, also called crawlers or spiders, to discover new and updated content across the web. These crawlers move from one page to another by following links. For example, when you publish a new blog post about digital marketing trends, the crawler will find it by following a link from your homepage or sitemap.
2. Indexing
Once crawlers discover a page, the information is stored in the search engine’s massive database — the index. Here, the content, keywords, images, and metadata are analyzed to understand the page’s topic. A page that is not indexed won’t appear in search results, making indexing crucial for visibility.
3. Ranking
When a user searches for something, the search engine sorts through its index and decides which pages best answer the query. Ranking is determined by many factors: keyword relevance, content quality, backlinks, page speed, and mobile-friendliness.
Modern search results (SERPs) include more than just links — featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, knowledge panels, and local packs. By optimizing content for these features, businesses can dramatically increase visibility, even if users don’t click through.
In short, search engines reward accessible, relevant, and high-quality content — making SEO essential for any website that wants to be discovered.
How to Learn Best SEO Practices
Learning SEO is most effective when you combine theory with practice and a commitment to continuous improvement. Search engine optimization is dynamic, and the best way to master it is to follow a structured process of observation, experimentation, and refinement.
1. Understand the Fundamentals
Start by building a clear understanding of the basics: how search engines crawl, index, and rank pages. Learn about keywords, on-page optimization, technical SEO, and link-building strategies. Having this foundation ensures you don’t get lost when trends or algorithms change.
2. Practice with Real Projects
Theory alone won’t make you skilled in SEO. Create or manage a project where you can apply what you learn — whether it’s a blog, a service page, or an e-commerce store. Use these as testing grounds to practice keyword placement, internal linking, and content structuring.
3. Observe and Analyze
Track how changes affect visibility and traffic. Pay attention to patterns such as which content attracts the most clicks or how adjusting meta descriptions improves engagement. This habit of monitoring results helps you develop intuition about what works.
4. Experiment with Strategies
Try different optimization techniques: write long-form guides, use FAQs, create infographics, or test voice-search-friendly content. Compare outcomes and refine your approach based on what brings consistent improvements.
5. Stay Adaptive
SEO evolves constantly, with changes in algorithms, user behavior, and technology. Instead of chasing quick hacks, focus on timeless practices like providing valuable content, improving user experience, and ensuring technical soundness.
In short: The best way to learn SEO is by doing and improving continuously. Apply strategies, observe results, adapt to changes, and over time you’ll develop the expertise to achieve sustainable rankings and growth.
Key Takeaways
SEO is not dead; it is more important than ever. It’s the foundation of digital visibility, credibility, and long-term growth. Organic rankings build trust, save costs, and deliver compounding returns over time. SEO requires patience, strategy, and consistency — but the rewards are worth it.
The most successful businesses combine SEO with SEM and PPC for a balanced strategy. Whether you’re planning to Start a New Business or grow an existing one, SEO future-proofs your digital presence.
In the digital age, people search before they buy, learn before they decide, and compare before they commit. If your business isn’t showing up, you’re invisible. Start applying SEO strategies today—optimize keywords, answer searcher intent, strengthen authority, and refine site structure—to make your brand rise above the noise. To expand your digital playbook, see the direct insights in best digital marketing strategies.

